Introduction
Most climate studies focus on future temperature projections due to greenhouse gas emissions, but this phenomenon also affects ocean wave patterns. Researchers from the University of the Basque Country have analyzed how the Earth’s atmosphere-ocean system absorbs temperature changes caused by climate change and impacts marine environments.
The Arctic: Less Ice, More Waves
An OECD report highlights the potential benefits of Arctic de-icing for goods transportation, estimating a 40% reduction in transit time between Asia and Europe. However, once the ice is partially gone, the researchers’ projections indicate a significant increase in wind and wave height by the end of the century, making navigation difficult even without ice.
- Question: What are the potential benefits of Arctic de-icing for maritime transportation?
- Answer: The OECD report suggests a 40% reduction in transit time between Asia and Europe due to Arctic de-icing.
- Question: How might increased wind and wave height in the Arctic impact maritime navigation?
- Answer: The significant increase in wind and wave height could make navigation difficult, even without ice.
The Mediterranean: Waves, Renewable Energy, and Security
The Mediterranean is a crucial link in another maritime route, carrying oil and gas from the Indian Ocean to Europe. The research shows an opposite behavior compared to the Arctic, with notable reductions in wind and wave height by the end of the century. The Mediterranean is expected to experience the most significant decreases in wind and wave height globally by 2100.
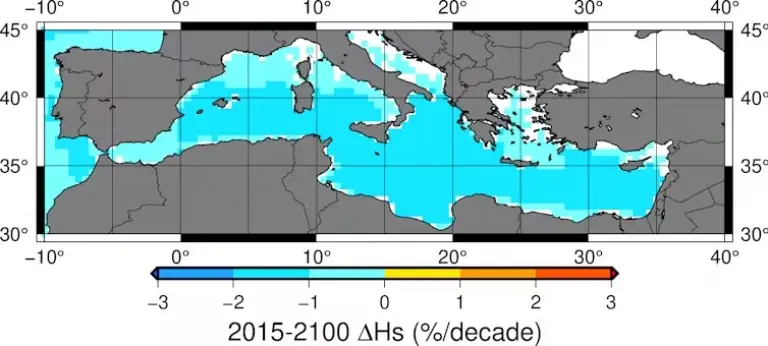
Proyecciones de cambios en la altura de ola hasta 2100 en el Mediterráneo.
The emerging implementation of wave energy extraction plants could face challenges, as the design of the first operational Mediterranean plant in Jaffa (Israel) relies on pistons whose performance depends on wave height. The predicted decrease in wave height presents new challenges for the technological development of similar plants in the Mediterranean.
- Question: How might changes in wind and wave height affect the development of wave energy extraction plants in the Mediterranean?
- Answer: The predicted decrease in wave height presents new challenges for the technological development of wave energy extraction plants in the Mediterranean.
Additionally, changes are expected in the wind sector and offshore parks planned for the coming decades, as they will have to face a decline in production due to reduced wind speed.






